According to Value Penguin, the average cost of home insurance in the U.S. is $1,516 per year. The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) reported a national average of $1,311 back in 2020, which means rates have increased by 15.66% within the last three years. Why has home insurance gone up? Various financial and environmental factors influence homeowners insurance rates, and prices may change over time due to a combination of these factors.
Why Has House Insurance Increased So Much?
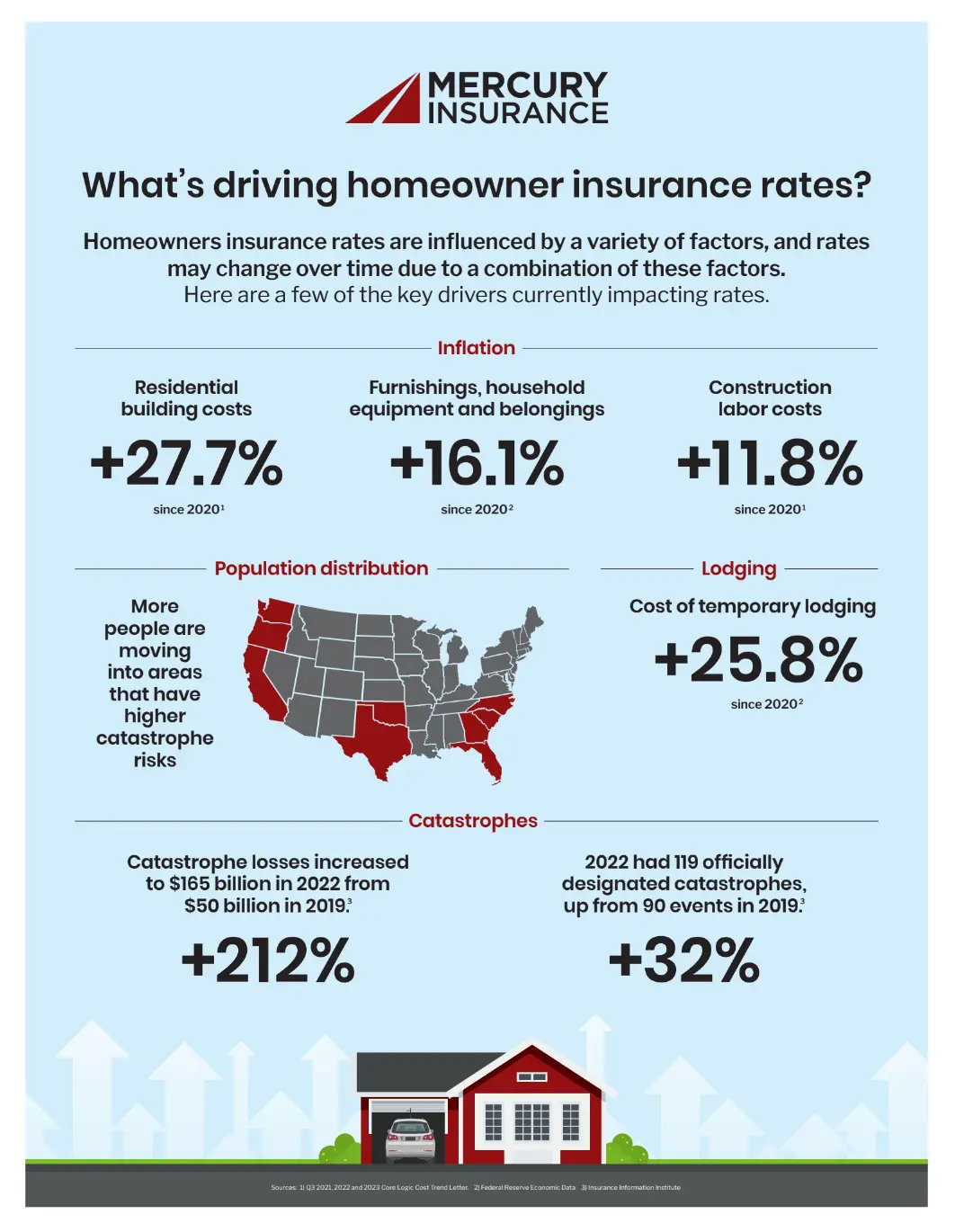
Here are a few key drivers that are currently impacting homeowners insurance rates:
Inflation
Inflation can increase the cost of goods and services, including construction materials and labor. Since 2020, residential building costs (+27.7%)1, construction labor costs (+11.8%)1, and the price of furnishings, household equipment, and belongings (+16.1%)2 have increased. As the general price of goods and services rises over time, insurance companies have to adjust their rates accordingly to maintain profitability. When the cost of living rises, the cost of homeowners insurance will inevitably rise with it.
Population Distribution
Population distribution can also impact insurance rates. More people are moving to areas prone to certain risks, such as wildfires, hurricanes, or flooding. Insurance companies may increase premiums to account for the higher likelihood of claims in regions such as California, Texas, Oklahoma, and Georgia.
Additionally, as more people move into urban areas and the demand for housing increases, higher property values are inevitable. As a result, this can lead to higher insurance premiums as the potential cost of replacing or repairing a home in these areas becomes much higher.
Catastrophes
The frequency and severity of catastrophes, such as wildfires and hurricanes, has increased over the past few years. For example, catastrophe losses increased to $165 billion in 2022 from $50 billion in 20193. Furthermore, 2022 had 119 officially designated catastrophes, a 32% increase from the 90 events in 20193.
These natural disasters can cause extensive damage to homes, resulting in more insurance claims. If there’s an increase in the frequency or severity of these events, insurance companies may raise premiums to offset the higher payouts they may need to make.
Lodging
The cost of lodging or temporary housing after a covered loss can also contribute to higher insurance premiums. Since 2020, the cost of temporary lodging has increased by 25.8%2. If your home is damaged and you need temporary lodging, your insurance company may have to cover these costs. As the cost of lodging increases, insurers may adjust premiums to cover rising claim expenses.
Factors Impacting Homeowners Insurance
Aside from the factors listed in the previous section, insurance companies assess several other factors to help determine your premium. Here are some of the key components that influence homeowners insurance rates:
Location
As mentioned before, living in a region prone to natural disasters can lead to higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of filing a claim. However, other geographical factors can impact rates, too. For example, a neighborhood’s crime level can influence insurance rates. Higher crime rates may increase premiums since there’s a greater chance of theft, vandalism, or other property-related crimes. Also, your home’s proximity to emergency services, such as fire departments and medical facilities, can affect your insurance rate. Generally, the closer you are to these services, the lower your premium, and vice versa.
Property Characteristics
Your property’s specific characteristics, such as age, size, construction materials, and overall condition all factor into insurance pricing. For example, if you have an older home or one built with materials susceptible to damage, you receive a higher premium since your home might be more expensive to rebuild or repair. You may also get a higher insurance premium if you have high-risk features like swimming pools, wood-burning stoves, and trampolines.
Home Security Measures
Investing in home security features, such as alarm systems, surveillance cameras, or fortified doors and windows, can positively impact your premium. Many insurance companies, including Mercury, offer discounts for being proactive about home security.
Credit Scores
Your credit score can affect insurance premiums since insurers use it to indicate risk. Maintaining a high credit score may lower premiums, as it suggests financial responsibility. To help improve your credit, pay your bills on time, use 30% or less of your available credit, and review your credit reports to track progress.
Claims History
If you have a track record of filing numerous claims, especially for similar incidents, insurers may label you as a high risk. As a result, you could face higher insurance rates. On the other hand, a clean claims history may lead to lower rates because you’re less risky to insure.
Deductibles
Your deductible — i.e., the out-of-pocket amount you pay before insurance kicks in — can also impact your insurance rate. Generally, choosing a higher deductible translates to a lower premium, and vice versa. However, if you select a higher deductible, make sure you can afford it should you need to file a claim.
Understanding Policy Coverage
Your insurance policy itself is another key factor that can determine your premium. Generally, the more coverage you have, the more you’ll pay for your premium.
You might ask yourself: What does my homeowners insurance cover? A typical policy protects your home’s structure, belongings, and liability. However, these coverages have limits — i.e., the maximum amount your insurer will pay for a covered loss. If the value of your home and possessions exceeds your policy’s limits, you might need to adjust your coverage accordingly so you receive adequate protection.
You can also add endorsements to your policy to tailor a coverage plan that suits your needs. For example, if you own high-value items like jewelry or antiques, opting for scheduled personal property coverage can help protect your valuables. These add-ons may raise your premium, but you can save a lot of money in the future if you experience a covered loss.
When considering additional coverage, think about the specific risks you face and whether these add-ons are worth the extra cost. Discuss your coverage needs with your insurance agent, as they can help you reap the benefits of homeowners insurance while staying within your budget.
Also, it’s a good idea to review your policy annually to ensure it aligns with your current needs and your property’s value. For instance, if you sold several high-value items, you may consider removing the scheduled personal property coverage to help reduce your premium.
Conclusion
While you can’t control certain factors that drive insurance rates, there are ways you can reduce your premium, such as bundling home and auto, choosing a higher deductible, or taking advantage of discounts. Reach out to a local agent today to see how you can get cheap homeowners insurance from Mercury.
Contact us today for a fast, free quote!
Sources
- Q3 2021, 2022, and 2023 Core Logic Cost Trend Letter
- Federal Reserve Economic Data
- Insurance Information Institute


